Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by Lenses
Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by Lenses: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Lens, Lens Maker's Formula, Power of Lens, Paraxial Rays, Optical Centre, Focal Length of Lens, Lens Equation, Thin Lens, Principal Axis of Lens, Refraction from Spherical Surface and, Focal Plane of a Lens
Important Questions on Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by Lenses
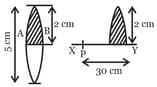
A converging lens of focal length 20 cm and diameter 5 cm is cut along the line AB. The part of the lens shown shaded in the diagram is now used to form an image of a point P placed 30 cm away from it on the line XY. Which is perpendicular to the plane of the lens. The image of P will be formed.
When the object is at distances u1 and u2 the images formed by the same lens are real and virtual respectively and of the same size. Then focal length of the lens is
A thin convex lens forms a real image of a certain object 'p' times its size. The size of real image becomes 'q' times that of object when the lens is moved nearer to the object by a distance 'a' find focal length of the lens?
Two thin lenses of power +6D and –2D are in contact. The focal length of the combination would be:
Define a method to measure the radii of curvature of lens.
Optical centre of a lens is important because it enables us to see the object more clearly without _____.
Is optical centre and centre of curvature same?
Explain optical centre of a lens with the help of proper diagrams?
What do you mean by focal plane of a lens ?
Transparent medium bounded by two refracting surfaces in which at least one of these is curved is a property of:
Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object which is kept at infinity from concave lens.
Magnification of a concave lens is
When the object is placed at focus of the concave lens, image is formed at _____.
What type of image is formed by concave lens ?
What is optical centre
A ray of light parallel to the principal axis of the lens passes through the principal axis after refraction through a convex lens.
The light ray coming along the principal axis of the lens remains undeflected.
Which of the following does not necessarily lie on the principal axis of the lens?
Define the principal axis of the lens. Answer in brief.
The image of the needle placed from a lens is formed on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. The displacement of the image, if the needle is moved by away from the lens in cm is
